A Sample of Tissue From a Suspect Area Can Be Further Divided Into Which of the Following?
Contemporary scientific discipline is a hotbed of cut-edge research. Astronomers across the globe take marveled at the start photographic show of a black hole. An anarchistic in vitro fertilization (IVF) technique has come under fire from medical professionals.
Elsewhere, scientists from Japan take fired explosives at an asteroid, and in Frg, they accept discovered a prehistoric molecule from the early years of universe. Setting bated the negative headlines—like the Israeli spacecraft that crash-landed on the Moon or the Indian missile examination that might have endangered the International Space Station—here are ten of the most fascinating breakthroughs to have made recent headlines.
10 Astronomers Have Bombed An Asteroid

A grouping of Japanese astronomers has decided to bomb the asteroid Ryugu, hoping it tin answer some fundamental questions about the origins of life on World. A cone-shaped instrument known every bit a "small comport-on impact" was sent hurtling into the asteroid, where it blasted out a crater using a baseball-sized wad of copper explosives.
The device was fired from the Hayabusa ii spacecraft—a pioneering exploration mission operated past the Japan Aerospace Exploration Bureau. The spacecraft volition head back to Ryugu at a later date to collect samples from beneath the asteroid'south surface that been uncovered in the blast.
Researchers predict there is a wealth of organic material and water from the nascency of the solar system preserved underground in the asteroid. By analyzing the samples from Hayabusa 2, they hope to gain a clearer understanding of the early stages of the solar system and of life on Globe.[1]
9 Tin We Sense of taste Smells?

It seems our tongues might exist more capable than nosotros originally realized. A inquiry squad from Philadelphia has suggested that receptor cells in the tongue are able to detect odors and smells. Their work is prompting experts to reassess whether gustation and smell are combined by the encephalon lonely or if there is some level of clan between the two signals.
The group, whose findings were published in the journal Chemic Senses, began past experimenting on receptors in genetically modified mice. Following this, they moved onto cells in humans, which displayed similar properties to the mice and were constitute to answer to aromatic compounds.
For now, it is far besides early to draw any physical conclusion, merely with further development, these ideas may be applied to persuade people to consume a healthier diet. Dr. Mehmet Hakan Ozdener, a specialist at the Monell Chemic Senses Middle, has suggested that mildly altering the scent of some foods could reduce saccharide intake.[2]
viii Molecule Detected From The 'Dawn Of Chemistry'
After decades of scouring the cosmos, experts take successfully detected the compound helium hydride, idea to be the first molecule formed in the history of the universe. Due to the obstructive effects of the Earth'southward atmosphere, researchers decided to take to the skies to make their landmark discovery. The Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, an airborne observatory built into a modified Boeing 747, was able to pick up infrared signals emanating from the prehistoric molecule.
In a period dubbed the "dawn of chemistry," effectually 100,000 years after the Large Bang, the universe had cooled to a low enough temperature that particles began to collaborate and coalesce. In this era, when light atoms and molecules first came into being, it was helium hydride that paved the mode for far more intricate interstellar structures to come up. Past continuing to investigate the elusive molecule, researchers are able to explore the expansion of the universe in its nascent stages.[3]
7 New Species Of Primitive Human Discovered
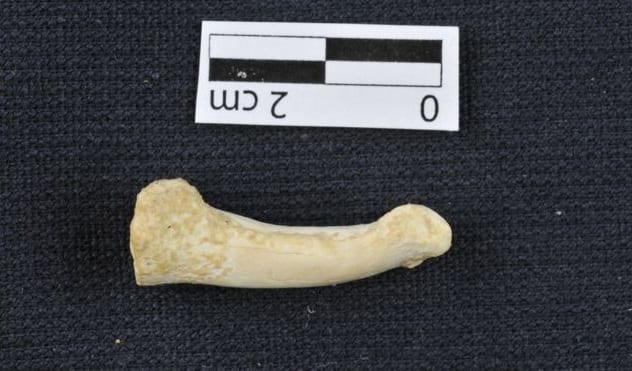
Another strand has been added to the history of human evolution. Remnants of an extinct relative have been found in Callao Cave on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The primitive species, known as Human luzonensis, is said to have resembled mod humans in some respects but in others was closer to our ancient ape-similar ancestors. On top of that, they are thought to have been competent climbers, as indicated past the curved basic in their fingers and toes.
The discovery poses a number of questions near the long and complex history of our species. With simply 13 teeth and basic on which to base their hypotheses, experts remain in the nighttime every bit to how Human being luzonensis came to be on the island in the first place. Furthermore, the species' features suggest that our ancient ancestors fabricated the journey out of Africa to Southeast Asia, an idea which contradicts current historical theories.[4]
6 Grunter Brain Revived Subsequently Expiry
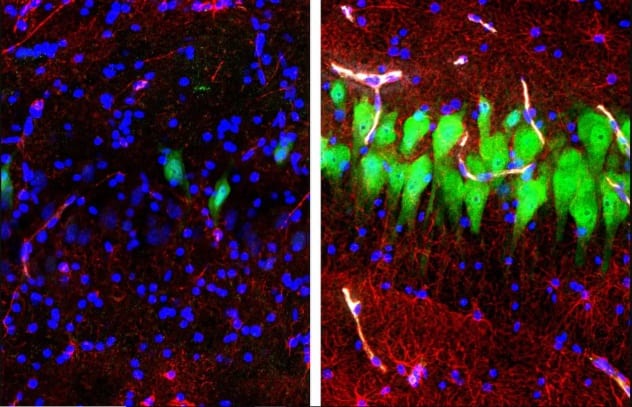
The zombie pigs are said to be among us. A team of neuroscientists from the Yale University School of Medicine have demonstrated that, in part, it is possible to revive a hog's brain hours after expiry. Their pioneering new system, BrainEx, has restored a number of basic functions to over 30 expressionless brains, such equally the power to absorb sugars and oxygen. (The left film higher up shows a dead brain, and the correct shows a partially reactivated encephalon.)
The engineering science involved in BrainEx sends an oxygen-rich solution pulsing through the pig'southward grey matter. This fluid partially revives the cells for a maximum of six hours, while also slowing down the procedure of deterioration later on decease. However, the brains are, by definition, still dead; there is no evidence of consciousness beingness reinstated.
This highly advanced inquiry presents an ethical quandary over whether it is right to experiment on semi-living beings. The National Institute of Health has been discussing the implications of BrainEx since 2022 via their Neuroethics Working Group and are wary of the possible consequences of using similar technology on humans.[five]
5 Scientists Create Transparent Organs
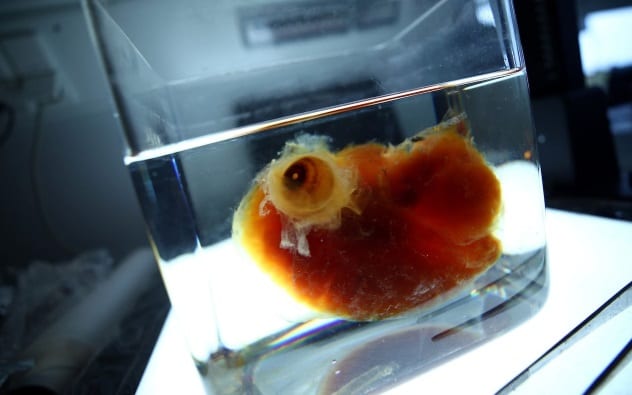
Organ transplants may before long go a thing of the past. For years, scientists accept strove to create fully operation artificial organs to address the significant dearth of donors. The dream is at present one pace closer, courtesy of Dr. Ali Erturk and his colleagues at the Ludwig Maximilians University in Munich.
The team has successfully developed a technique to mode transparent human organs, with an aim to further empathize their elaborate inner structures. Organic solvents are used to remove fats and pigments without disturbing any of the tissue underneath. The uncovered organs tin be explored in intricate detail using a light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation scanner, which allows scientists to build up a complete structural image of the trunk part.
Erturk is confident that, as technology improves, these scans can be used equally blueprints to produce iii-D bioprinted replica organs. The team hopes to take constructed a 3-D printed kidney by 2025.[6]
4 Obesity-Resistant Genes Discovered

The link betwixt genetics and body mass has been known for many years, but now scientists at Cambridge University have identified exactly which genes go along people slim. Around iv million people in Britain, six per centum of the population with European ancestry, have a specific Deoxyribonucleic acid coding that prevents them from gaining big amounts of weight.
Previous studies discovered that the gene MC4R controls a protein known as melanocortin 4, a encephalon receptor associated with appetite. Participants in this experiment with a specific strand of MC4R displayed more restraint in their appetites, making them far less likely to suffer from obesity or type ii diabetes. This deepened understanding of genetics opens up the possibility of a slimming medication to combat rise levels of obesity.[7]
3 Memory Loss Reversed

Past stimulating the brain with electrical pulses, scientists are able to temporarily offset the debilitating effects of retentivity loss. With age, vital cognitive networks in the brain begin to lose their synchronicity. This leads to the deterioration of the working memory—the short-term processing system that plays a key role in tasks like facial recognition and arithmetics.
At present, neuroscientists at Boston University have found that noninvasive electrical stimulation appears to meliorate the connection between these networks. The researchers reported that a study group of 60- to 76-year-olds performed significantly better in a serial of working memory tasks after around half an hour of pulse treatment. Those with the most pronounced memory problems showed the biggest improvements.
Further clinical trials are needed to determine whether this stimulation is a viable method for combating retentiveness loss or dementia.[viii]
2 Baby Born With DNA From Three People

In a quantum moment for in vitro fertilization, a infant has been born in Hellenic republic with DNA from iii unlike people. The newborn boy was conceived using the mitochondrial donation technique, in which the intracellular structure of the mother's egg is modified slightly using a second donor egg. During the technique, the mitochondria—tiny, floating structures that provide ability to the cell—from the female parent's egg are replaced by that of a donor. While the vast majority of the babe's genetic textile has been passed down from his parents, an extremely pocket-sized amount of his Dna—around 0.2 percent—originates from the donor.
Doctors merits this is the kickoff time that mitochondrial donation has been applied to combat fertility issues. Spanish embryologist Nuno Costa-Borges has labeled the good for you birth a "revolution in assisted reproduction" and claims that it has the potential to aid a multitude of would-be mothers in the future.
Nonetheless, critics of the treatment are alert women to continue with caution. Reproductive practiced Tim Kid has explained how little is known nigh the risks or benefits of the technique, dismissing Costa-Borges'south claims every bit unfounded in testify.[nine]
1 First epitome Of A Black Hole

For the by century, the merely show astrophysicists have had for the beingness of black holes has been scientific theories and indirect observations. The cosmic giants have a gravitational attraction so powerful that cipher can escape their immense pull, and their existence has been incredibly challenging to verify. And withal, in spite of the major difficulties, scientists have managed to generate an paradigm of one.
The picture in question is of the fiery disk of accreted gas surrounding the black pigsty at the core of the Messier 87 galaxy. With a diameter of 38 billion kilometers (23.vi million mi), the active supermassive colossus lurks 55 million light-years from our planet. The black hole itself is impossible to literally "see," but the dark area at the center of the ring corresponds to its shadow.
To capture the image, a job described by leading astrophysicist France Cordova every bit "Herculean," scientists deployed the Outcome Horizon Telescope (EHT), a global network of high-precision radio telescopes.[ten] This Herculean task required a Herculean amount of data, so much that it was incommunicable to transfer over the Cyberspace. Instead, half a ton of hard drives had to be flown to a central location, where the readings were combined using state-of-the-art processing techniques.
The image appears to verify the outset predictions of black holes made past Einstein's full general theory of relativity, which addresses the distortion of space and time acquired by immense, massive objects. The EHT researchers now have their sights on Sagittarius A—the supermassive beast at the heart of the Milky way.
mcnaughtonsough1988.blogspot.com
Source: https://listverse.com/2019/05/13/10-recent-scientific-breakthroughs-and-discoveries/
0 Response to "A Sample of Tissue From a Suspect Area Can Be Further Divided Into Which of the Following?"
Post a Comment